
MMWR: Lessons from a Salmonella Outbreak at a County Fair
A 2024 outbreak of Salmonella enterica serotype Agbeni sickened 13 attendees at the Brown County Fair in Mount Sterling, Illinois, highlighting overlooked public health risks at community events. Investigators identified a beer cooler—reused over multiple days without cleaning—as the shared exposure among cases, including attendees who did not eat fair food.
Laboratory confirmation, ep…

New Study Highlights Long-Term Brain Risks for Football Players
Recent research in JAMA Network Open reinforces the connection between American football and long-term brain health risks. Analyzing hundreds of men aged 40 and older, the study found that anyone with football experience—ranging from youth leagues to professional play—tended to score lower on cognitive tests, report more personal cognitive concerns, and experience more severe depressive symptom…

Screen Time is Increasing for People Over 60
Recent research shows that adults over 60 are spending more than half of their daily leisure time on screens, including tablets, smart TVs, and e-readers. Public health experts note that older adults primarily use technology for practical purposes—news, information, and staying connected with family—rather than social media engagement.
While increased screen time can support independence, red…

What’s Ahead for NPHIC in 2026
As we move further into 2026, NPHIC wants to thank our members for your continued leadership and dedication to public health communication. In a rapidly evolving information landscape, we remain deeply committed to supporting your work through practical tools, professional development, and opportunities for connection.
This year, we are exploring a potential strategic partnership with the Pub…

NCHCMM Conference Update for Public Health Communicators
As a proud co-host of the National Conference on Health Communication, Marketing, and Media (NCHCMM), NPHIC would like to share a brief conference update with our community. In keeping with the conference’s every-other-year cadence, the next full, in-person NCHCMM will be held in July 2027. There will not be a full, in-person conference in 2026.
Throughout 2026, we’ll be exploring additional…

New Voices from the Field Podcast - Syphilis During Pregnancy: The Role of Public Health Communication in Prevention
Recorded live at the 2025 National Conference on Health Communication, Marketing, and Media (NCHCMM) in Atlanta, this new episode of Public Health Speaks features Michael McNair of the New York State Department of Health’s Office of Sexual Health and Epidemiology. McNair discusses his campaign, Syphilis During Pregnancy: The Role of Public Health Communication in Prevention, developed in respon…

Biohackers and Wellness Influencers are Pushing Nicotine as Part of Their ‘Stacks’
Nicotine is being rebranded by startups and influencers as a cognitive and performance enhancer, raising new public health concerns. Wellness marketing and social media narratives increasingly position nicotine pouches, patches, and drinks as tools for focus, energy, or lifestyle optimization, even among nonsmokers.
Experts caution that evidence for cognitive benefits in healthy individuals i…

Early Prenatal Care Declining in US: CDC Data
A recent CDC analysis indicates a decline in early prenatal care initiation in the United States, with the proportion of mothers beginning care in the first trimester falling from 78.3% in 2021 to 75.5% in 2024. Concurrently, second-trimester starts and late or no care both increased. The findings underscore the established importance of early prenatal care, which is associated with healthier p…
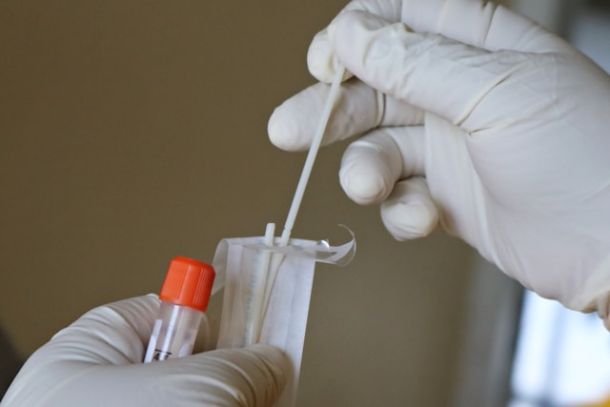
Using Saliva to Detect Disease Holds Promise, But It's Not Perfected Yet
Emerging salivary diagnostics offer promising opportunities for earlier, more accessible disease detection. Already used to identify HIV and COVID-19, saliva-based tests are being developed to detect conditions such as oral cancers, diabetes, and other chronic diseases. Public health leaders note their potential to expand preventive care, reduce barriers for rural and underserved populations, a…

